Cybersecurity Challenges in Online Banking: Protecting Customer Data
Introduction
In our computer-driven era, banks have increasingly moved their services online for faster and easier access. Yet, this convenience comes with a risk: the threat of cyber attacks that can lead to the loss or theft of customer data. In 2022, there were 1829 reported cyber incidents in the financial industry. Banks hacked today often, so it’s clear that having strong security measures is crucial for keeping customers’ trust and securing their personal and financial information.
In this article, you’ll learn more about the importance of cybersecurity for banking apps and platforms. You’ll also discover common cybersecurity challenges and how to address them.
Why Cybersecurity is Essential for Banking Apps and Platforms?
The digitization of financial services has escalated the need for advanced cybersecurity for financial services. Criminals are drawn to banking networks because they hold a lot of sensitive data. Without strict security measures in place, sensitive data is vulnerable to illegal access and misuse.
- Trust and reputation: Customers must believe that their financial data is safe; otherwise, the bank’s reputation will be irreversibly harmed.
- Regulatory compliance: Banks are subject to stringent regulatory regulations to safeguard client data and privacy.
- Financial stability: Cyber attacks can lead to substantial financial loss both for the customers and the banks themselves.
- Operational continuity: Robust cyber security in banking ensures that banks can maintain operations without interruptions caused by cyber threats.
Enhancing bank security systems is not just about preventing banking data breaches but rather about safeguarding the very integrity of the financial sector.
One of the ways to ensure the high security of your banking app is through banking APIs. It implies that you adopt a functionality, such as two-factor authentication, from an external provider that handles all the technical aspects for you. Bank API integration is an easy way to enrich your platform or app with added security features. Additionally, not only can you request bank APIs for security, but you can also ask for financial services APIs that will enable you to start offering diverse services, like trading, accounting, cross-border SME transacting, etc. It’s safe to claim that bank integration APIs are widespread, reliable, and extensively used.
Ensure that you request the APIs from a trusted provider. It’s even better if a partnering company can help you with the integration of the API into your digital infrastructure, as it’s not always as easy as adding a few lines of code.
Common Cybersecurity Challenges in Online Banking and Solutions to Them
The issue of cybersecurity for financial services is complicated and difficult, as bank accounts and finance are likely to be among the most popular targets for fraudsters. Here are some of the most prevalent banking cybersecurity issues and solutions to them:
Phishing Attacks
Fraudsters frequently employ phishing to deceive banking clients into disclosing personal information. They may utilize bogus websites, emails, or messages that appear to be from the bank and solicit clients to provide sensitive information. The technique of phishing attacks is depicted in the graphic below:
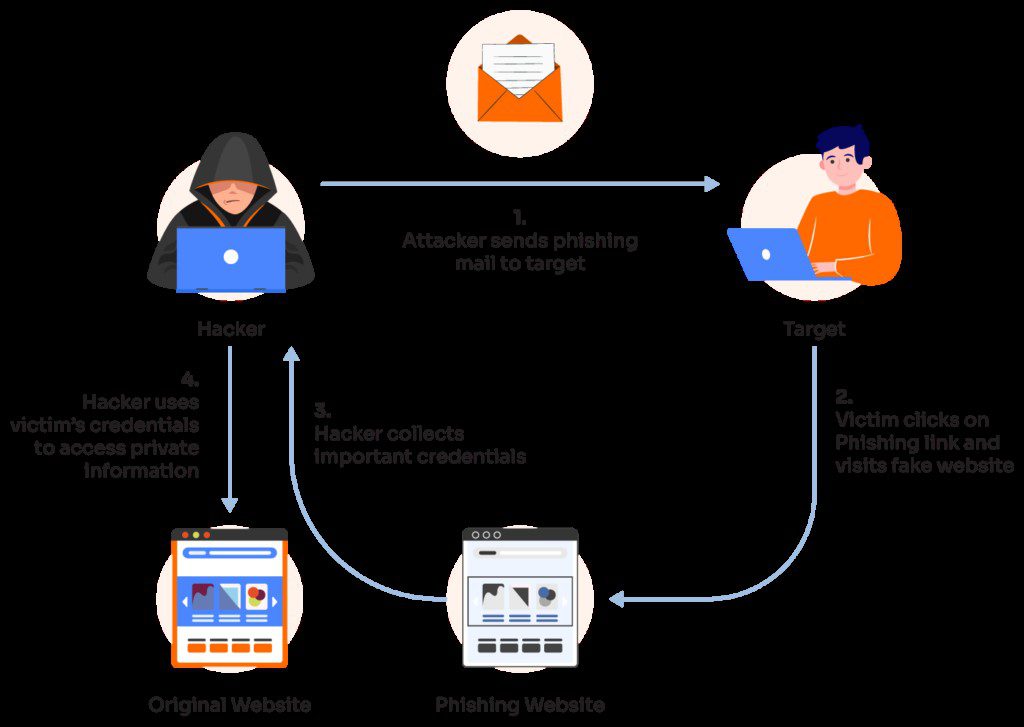


Solution: To counter this, banks need to continuously educate their customers about the dangers of phishing and how to recognize such scams. They should encourage customers to check the legitimacy of banking communications. Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of protection, making it more difficult for attackers to obtain access even if they know some consumer information.
Malware and Ransomware
Malware can secretly penetrate banking systems to steal sensitive data, while ransomware takes data hostage, demanding payment to restore access, thus disrupting banking operations.
Solution: Banks should invest in advanced threat detection and antivirus software to identify and stop malware infections. Regularly updating and patching systems can prevent known vulnerabilities from being exploited. Backing up data frequently ensures that the bank can restore information with minimal loss in case of a ransomware bank cyber attack.
Insider Threats
Not all threats are external; sometimes, employees with access to sensitive systems and data might misuse their privileges, intentionally or accidentally.
Solution: A key preventive measure is implementing strict access controls, ensuring that employees can only reach data necessary for their work. Regular audits and monitoring of employee activities can detect potential misuse, helping banks act quickly to prevent data leaks or theft.
DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks are designed to bring down financial websites by flooding them with traffic, rendering services inaccessible to genuine customers. The method of DDoS assaults is depicted in the graphic below:
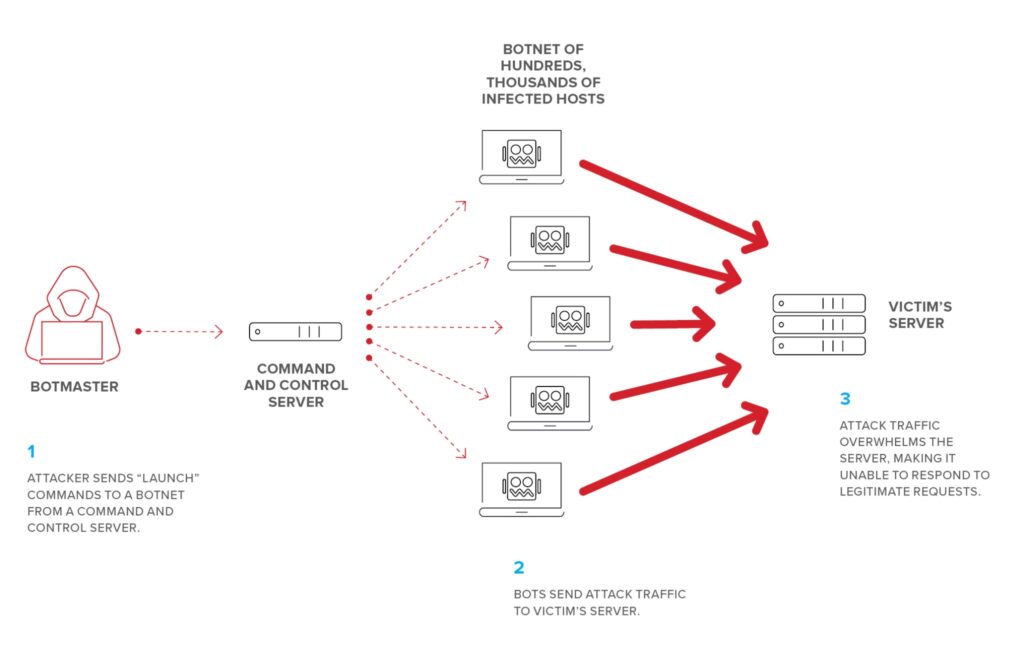


Solution: Banks can protect against DDoS attacks by increasing the robustness of their IT infrastructure to handle sudden increases in traffic. They can also use specialized DDoS prevention tools that detect and filter out malicious traffic.
API Vulnerabilities
As banks integrate more services with third parties, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) can become a weak link, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive data if not properly secured.
Solution: Conducting comprehensive security testing and regular security audits on all APIs can uncover vulnerabilities. Banks should also implement strong authentication methods and encrypt API traffic to ensure that only authorized applications can access the bank’s systems.
Data Breaches
Data breaches can occur due to various vulnerabilities, leading to the exposure of customer information and potentially resulting in financial fraud.
Solution: Encryption of data at rest and in transit is essential to protect sensitive information. Employing a bank security system for real-life monitoring can help in the early detection of unusual activities that may indicate a breach, allowing banks to respond promptly.
Mobile Banking Threats
The popularity of mobile banking has made mobile platforms an attractive target for cybercriminals, who exploit security weaknesses to steal data or money.
Solution: Ensuring mobile banking apps are built with security in mind is crucial. This includes secure coding practices, frequent updates, and regular security audits. Additionally, educating customers about the safe usage of mobile banking apps, like downloading apps only from trusted sources, is important.
Spoofing
Spoofing attacks involve forging the sender’s address in communications, making them appear as if they come from a trusted source, such as a bank.
Solution: Solutions involve implementing email validation systems such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) to prevent spoofing. Banks should also encourage customers to verify the authenticity of communications before responding.
Final Take
Strong cybersecurity in banks is a must. As cyber threats become more complex, banks are constantly at risk. They need solid strategies and ongoing security efforts to keep attacks at bay. This not only helps to prevent hacking attempts but also maintains the trust that customers place in their banks.
With the constant advancement of technology, banks must continuously evolve their cybersecurity practices to minimize risks of potential security breaches.
Related Apps
Latest News
- Navigating the Tech Job Market: Top Skills Students Should Develop
- Top 9 spy apps for iPhone: monitor calls, messages, and free trial
- Cybersecurity Challenges in Online Banking: Protecting Customer Data
- 12 best phone tracker app without permission in 2023
- How to track an iPhone without an app
- 7 Tips That Will Make You a Tech Guru







